Pump systems play a crucial role in various industries, serving as the backbone of numerous applications, from water supply and wastewater management to chemical processing and agriculture. According to a report by the Global Market Insights, the global pump market size is expected to exceed $70 billion by 2026, driven by increased demand in industrial automation and energy efficiency. This highlights the significance of understanding pump systems and their operational dynamics across different sectors.
One of the fundamental aspects of pump systems is their ability to move fluids efficiently and effectively. Different applications require tailored pump solutions, which can range from centrifugal and positive displacement pumps to submersible and diaphragm types. Research from the Hydraulic Institute indicates that properly designed pump systems can enhance energy efficiency by up to 30%, underscoring the importance of selecting the right pump technology for specific requirements. This efficiency not only contributes to operational cost savings but also aligns with global sustainability goals.
As industries continue to innovate and evolve, the performance, reliability, and adaptability of pump systems become increasingly critical. The integration of advanced technologies, such as IoT and automation, is revolutionizing how these systems are monitored and controlled, further optimizing their functionality. Understanding the diverse applications and working principles of pump systems is essential for professionals looking to leverage the benefits of these vital components in their operations.

A pump system is a crucial mechanism designed to move fluids from one location to another. It typically consists of several basic components, including a pump, motor, piping, and control systems. The pump serves as the heart of the system, utilizing various mechanisms—such as centrifugal force or positive displacement—to create the necessary pressure for fluid movement. The motor provides the energy to drive the pump, while the piping facilitates the flow of the fluid, connecting various system components. Control systems regulate parameters such as flow rate and pressure, ensuring the pump operates efficiently and effectively according to the specific requirements of each application.
Different applications utilize pump systems in varied ways, highlighting their versatility. In industrial settings, pumps are essential for processes such as chemical mixing, wastewater management, and cooling water circulation. In residential applications, they help with water supply, irrigation, and basement drainage. Furthermore, in the medical field, pumps play a vital role in intravenous therapy and drug delivery systems. Each application demands specific requirements in terms of design, efficiency, and reliability, showcasing the importance of understanding pump systems and their fundamental components in addressing diverse fluid movement challenges.
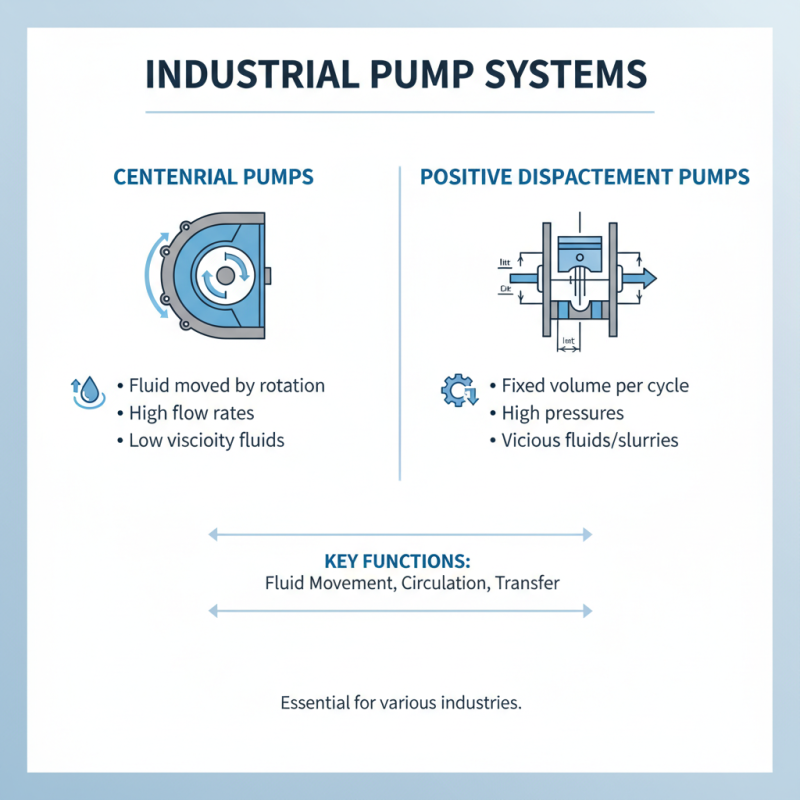
Pump systems are essential components in various industries, serving critical functions in fluid movement. The two primary types of pump systems are centrifugal and positive displacement pumps, each with distinct operational principles and applications.
Centrifugal pumps utilize rotational energy to move fluid, employing an impeller to impart velocity to the liquid, which is then converted to pressure. These pumps are well-suited for applications involving large volumes of fluid at relatively low viscosity, such as water supply systems or chemical processing. According to a report by the Global Market Insights, the centrifugal pump market size was valued at over $20 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow steadily, driven by the increasing demand for efficient water management systems.
Conversely, positive displacement pumps operate by trapping a fixed amount of fluid and forcing it through the discharge pipe. This design allows them to handle high-viscosity fluids and provide a consistent flow rate regardless of pressure changes. Applications of positive displacement pumps are prevalent in sectors such as oil and gas, food processing, and pharmaceuticals. The market for these pumps is also on the rise, with estimates suggesting a growth forecast to surpass $10 billion by 2025, as industries seek more precise and controlled pumping solutions. Understanding the unique characteristics and optimal use cases for each type of pump system is essential for engineers and facility managers in selecting the right equipment for their specific needs.
Pump systems are integral to numerous industrial processes and manufacturing applications, facilitating the transfer of fluids in a controlled and efficient manner. According to a report by the Hydraulic Institute, the pump industry is projected to grow significantly, with the global market expected to reach approximately $80 billion by 2025. This growth is driven by the increasing demand for advanced pumping solutions in sectors such as oil and gas, water treatment, food processing, and chemical manufacturing.
In industrial settings, pump systems are used for various purposes, including the transport of chemicals, cooling water circulation, and wastewater management. For instance, in the chemical manufacturing industry, centrifugal pumps are widely employed to move corrosive substances safely. A study from the American Society of Mechanical Engineers highlights that efficient pump systems can lead to energy savings of up to 20%, which can substantially reduce operational costs for manufacturers. Moreover, the integration of intelligent pumping technologies enables predictive maintenance, further enhancing the reliability and efficiency of the systems.
Furthermore, in the food processing sector, pumps play a crucial role in maintaining hygiene and quality standards during production. Positive displacement pumps, in particular, are favored for handling viscous materials like sauces and creams as they provide a consistent flow rate and minimize shear stress on sensitive ingredients. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the food and beverage pump market alone is expected to reach $12 billion by 2024, underscoring the vital role pump systems play in sustaining production efficiency and product quality in this industry.
Efficiency metrics play a crucial role in evaluating pump performance and energy consumption in various applications. Understanding these metrics allows users to optimize system designs and make informed decisions regarding pump selection and operation. Key performance indicators such as flow rate, total dynamic head, and pump efficiency (%) help assess how effectively a pump converts input energy into fluid movement. Monitoring these metrics can significantly impact energy consumption, as even small variations in efficiency can lead to substantial differences in operational costs over time.
Moreover, the energy consumption of a pump system is influenced by factors such as the type of pump, the nature of the fluid being pumped, and the overall system design. By analyzing energy use in terms of specific metrics like horsepower per flow rate or the life cycle cost of energy consumption, operators can identify opportunities for improvement. Implementing technologies such as variable frequency drives (VFDs) and enhancing hydraulic design can lead to notable efficiency gains. Evaluating and managing these efficiency metrics is essential for achieving maximum operational efficiency, reducing costs, and minimizing environmental impact in pump applications across various industries.
As the global demand for energy efficiency and sustainability increases, the pump industry is undergoing significant innovations in technology. According to a report by Market Research Future, the global pump market is projected to reach approximately $90 billion by 2026, expanding at a CAGR of around 5.3%. This growth is primarily driven by advancements in pump design and materials that enhance performance while reducing energy consumption. Notable innovations include the development of smart pumps, which incorporate IoT technology for real-time monitoring and optimization of operations, leading to reduced waste and improved maintenance schedules.
Sustainable solutions are also becoming a focal point of pump technology. Recent studies indicated that energy-efficient pumps can reduce energy usage by up to 50% compared to traditional models. Furthermore, integrating renewable energy sources into pumping systems not only minimizes carbon footprints but also aligns with global sustainability goals. The adoption of advanced materials, such as composite polymers, is leading to lighter and more durable pumps that are less prone to corrosion, thus extending their operational lifespan while decreasing environmental impact. The future of pump technology is not just about enhanced efficiency; it's about creating systems that contribute to a more sustainable future, responding directly to changing environmental demands and regulatory standards.
The chart above illustrates the focus areas for future innovations in pump technology, highlighting the shift towards energy efficiency and automation, while emphasizing the significance of sustainability and maintenance innovations in the industry.





sale@harbertpump.com,
sale@harbertpump.com,
sale@harbertpump.com,
sale@harbertpump.com,
sale@harbertpump.com